The incredible benefits of fiber to human health and wellbeing
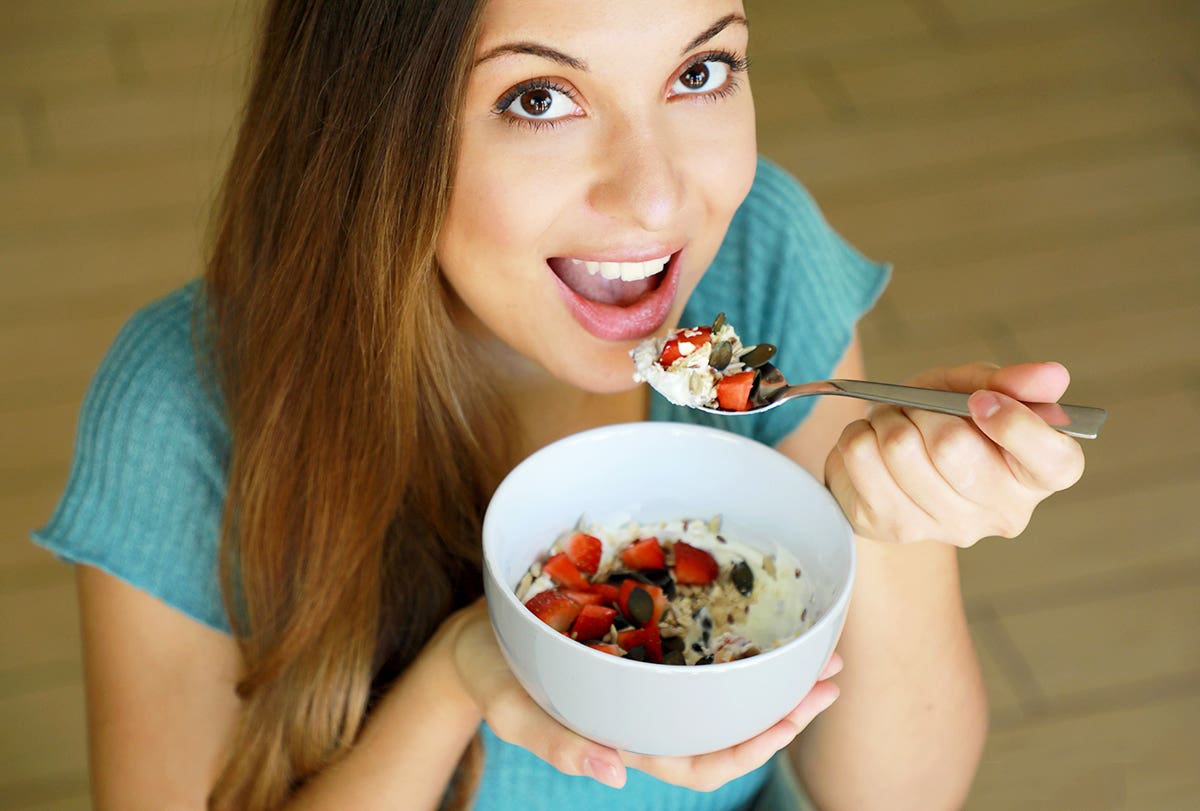
Fiber is a complex carbohydrate that is found in plant foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds.

[Feb. 21, 2023: Staff Writer, The Brighter Side of News]
Fiber is a complex carbohydrate that is found in plant foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. (CREDIT: Creative Commons)
Fiber is a type of carbohydrate that cannot be digested by human enzymes, and therefore it passes through the digestive system mostly intact. It is a complex carbohydrate that is found in plant foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. There are two types of fiber: soluble and insoluble. Soluble fiber dissolves in water, while insoluble fiber does not. Both types of fiber have unique health benefits, but they are primarily associated with improving gut health.
In this article, we will explore the various benefits of fiber in gut health, including how fiber promotes digestive health, protects against chronic diseases, and contributes to overall wellbeing.
Promoting Digestive Health:
Fiber is known for its ability to promote digestive health. One of the primary ways that fiber achieves this is by promoting regular bowel movements. Insoluble fiber, in particular, adds bulk to stool, which makes it easier to pass. This can help prevent constipation, a condition where bowel movements are infrequent or difficult to pass. In addition to promoting regular bowel movements, fiber can also help prevent other digestive issues such as hemorrhoids, diverticulitis, and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
Fiber can also help maintain a healthy gut microbiome, which is the collection of microorganisms that reside in the digestive tract. These microorganisms play an important role in maintaining overall health, and they can influence various functions throughout the body, such as the immune system, metabolism, and brain function.
Related Stories
Soluble fiber, in particular, is beneficial for the gut microbiome because it can be fermented by gut bacteria. During fermentation, the bacteria break down the fiber and produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which provide energy to the cells in the colon and help maintain a healthy gut environment. SCFAs also have anti-inflammatory properties that can help prevent chronic diseases.
Protecting Against Chronic Diseases:
Fiber has been associated with a decreased risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. One of the ways that fiber may protect against these diseases is by reducing inflammation in the body. Inflammation is a natural response that occurs when the body is injured or infected, but chronic inflammation can lead to damage to the body's tissues and cells, and it has been linked to many chronic diseases.
Fiber can help reduce inflammation by feeding the gut microbiome. When fiber is fermented in the colon, it produces SCFAs, which can reduce inflammation throughout the body. SCFAs have been shown to decrease the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the body, which are proteins that can promote inflammation. In addition to reducing inflammation, fiber can also help regulate blood sugar levels, which can help prevent diabetes. Soluble fiber, in particular, can slow down the absorption of glucose in the bloodstream, which can help prevent spikes in blood sugar levels.
Potential pathways through which SCFAs influence gut-brain communication. (CREDIT: Frontiers)
Fiber has also been associated with a decreased risk of certain types of cancer. This may be due to the fact that fiber can promote regular bowel movements, which can help reduce the amount of time that potential carcinogens are in contact with the cells in the colon. Fiber can also help reduce inflammation, which can prevent the development of cancer cells. In addition, fiber can help regulate hormones, which can help prevent hormone-related cancers such as breast and prostate cancer.
Contributes to Overall Wellbeing:
Fiber is an important nutrient that can contribute to overall wellbeing. One of the primary ways that fiber contributes to wellbeing is by promoting satiety, which is the feeling of fullness after a meal. This can help prevent overeating and contribute to weight management. Fiber-rich foods tend to be more filling and satisfying than foods that are high in fat or sugar. Soluble fiber, in particular, has been shown toslow down the digestion of food, which can help people feel fuller for longer periods of time.
In addition to promoting satiety and weight management, fiber can also improve heart health. Studies have shown that consuming a diet high in fiber can lower cholesterol levels, which can help reduce the risk of heart disease. This may be due to the fact that fiber can bind to cholesterol in the digestive tract and prevent it from being absorbed into the bloodstream. Fiber can also help regulate blood pressure, which is another important factor in maintaining heart health.
Fiber can also contribute to overall wellbeing by improving mental health. The gut-brain axis is a communication pathway between the gut and the brain, and it plays an important role in mental health. The gut microbiome can influence the production of neurotransmitters, such as serotonin, which is a key neurotransmitter involved in mood regulation. Studies have shown that consuming a diet high in fiber can improve the gut microbiome, which can in turn improve mental health.
How to Increase Fiber Intake:
Despite the many benefits of fiber, many people do not consume enough of it. The recommended daily intake of fiber is 25 grams for women and 38 grams for men. However, studies have shown that the average intake of fiber in the United States is only 15 grams per day.
Fortunately, there are many ways to increase fiber intake. One of the easiest ways to do so is to consume more fruits and vegetables. Fruits and vegetables are high in fiber, as well as many other important nutrients. Whole grains, such as brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread, are also good sources of fiber. Legumes, such as beans, lentils, and chickpeas, are also high in fiber.
It is important to increase fiber intake gradually, as consuming too much fiber too quickly can lead to digestive discomfort such as bloating, gas, and diarrhea. It is also important to drink plenty of water when consuming a high-fiber diet, as fiber absorbs water and can lead to constipation if not enough water is consumed.
Conclusion:
Fiber is an important nutrient that is essential for gut health. It promotes regular bowel movements, maintains a healthy gut microbiome, protects against chronic diseases, and contributes to overall wellbeing. Despite the many benefits of fiber, many people do not consume enough of it. It is important to increase fiber intake gradually and to consume plenty of water when consuming a high-fiber diet. By consuming a diet rich in fiber, people can improve their digestive health, protect against chronic diseases, and contribute to their overall wellbeing.
Note: Materials provided above by The Brighter Side of News. Content may be edited for style and length.
Like these kind of feel good stories? Get the Brighter Side of News' newsletter.