Study finds video games improve mental well-being
Groundbreaking research reveals video games can improve mental well-being, challenging stereotypes. Learn how gaming affects health and life satisfaction.
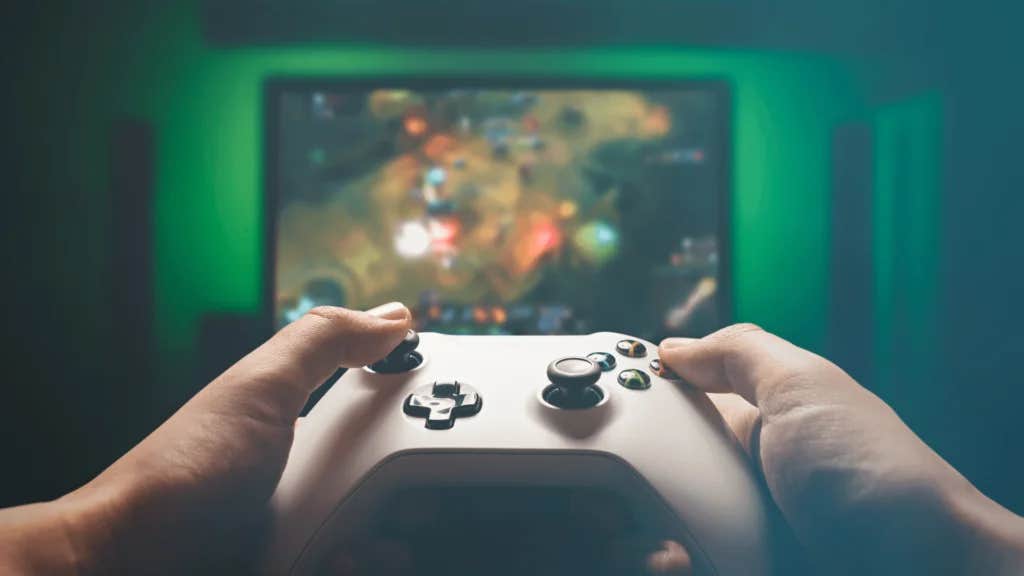

New research challenges stereotypes about video gaming’s effects. Discover how gaming consoles like the Nintendo Switch improve mental health and life satisfaction. (CREDIT: Creative Worlds)
As digital devices permeate every corner of life, video games have become both a popular pastime and a point of contention.
Public concerns about gaming’s impact on mental well-being often cast these activities in a negative light. In 2019, the World Health Organization (WHO) classified "gaming disorder" as a mental health condition, sparking debates about its implications.
Critics argue this stigmatizes players, especially younger individuals for whom gaming is a cultural norm. Despite the controversy, new research suggests gaming may offer unexpected benefits to mental health.
Shifting Perspectives on Gaming’s Effects
The COVID-19 pandemic dramatically reshaped daily life, including how people relax and connect. During this period, video games gained prominence as a safe, socially distant way to spend time.
Globally, gaming participation surged, with nearly three billion people actively engaging. This sharp rise reignited discussions about whether gaming contributes positively or negatively to psychological health.
Over the years, researchers have studied gaming’s effects on aggression, cognitive function, and mental well-being. Early studies, particularly in the 2000s, linked violent games to heightened aggression. However, subsequent investigations have largely discredited these claims, finding no definitive connection.
Recent academic focus has shifted to exploring how gaming affects mental well-being. The results are mixed: some studies associate gaming with improved mental health, while others highlight potential risks like addiction or negative emotions.
Many studies examining gaming’s effects rely on observational methods, which reveal associations but not causation. Experimental studies, though more controlled, often fail to replicate natural gaming environments. For example, artificially limiting gameplay in a lab may not accurately reflect real-life habits.
Moreover, confounding factors, such as individual personality traits or socioeconomic conditions, complicate efforts to draw concrete conclusions. This methodological inconsistency underscores the need for innovative approaches to studying gaming’s real-world impacts.
Related Stories
In a pioneering study, researchers from Japan took advantage of a unique natural experiment. During the COVID-19 pandemic, supply chain disruptions limited access to gaming consoles like the Nintendo Switch and PlayStation 5 (PS5).
Japanese retailers used lotteries to allocate these devices, creating an unintentional randomized distribution of console ownership. Researchers leveraged this situation to analyze the causal relationship between gaming and mental well-being.
The study, published in Nature Human Behaviour, analyzed 97,602 survey responses from individuals aged 10 to 69 in Japan. Using advanced statistical methods, including causal forest machine learning algorithms, the team examined the impact of console ownership on mental health and life satisfaction.
The findings revealed that owning a Nintendo Switch improved mental health by 0.60 standard deviations, while owning a PS5 led to a smaller improvement of 0.12 standard deviations. Additionally, PS5 ownership boosted life satisfaction by 0.23 standard deviations.
Interestingly, the benefits varied by demographic factors. Adolescents and females experienced greater psychological gains from owning a Nintendo Switch compared to a PS5. These differences underscore the importance of considering specific gaming platforms and genres when evaluating their effects.
Lead researcher Hiroyuki Egami, Ph.D., from Nihon University, emphasized the study’s significance in challenging stereotypes about gaming. “Our findings challenge common stereotypes about gaming being harmful or merely providing temporary euphoria,” Egami stated. “We’ve shown that gaming can improve mental health and life satisfaction across a broad spectrum of individuals.”
The study’s innovative design allowed researchers to move beyond traditional observational methods. “Many earlier studies drew conclusions from correlational analysis with observational data, which can’t distinguish between cause and effect,” Egami explained. “Our natural experimental design allows us to confidently say that gaming actually leads to improved well-being, rather than just being associated with it.”
Md. Shafiur Rahman, Ph.D., from Hamamatsu University School of Medicine, highlighted the study’s relevance to policymakers. “This study’s robust methodology challenges preconceptions about gaming’s negative impacts. It highlights the need for a more nuanced approach in studying digital media’s effects on health,” he said.
The research also questioned long-standing assumptions about gaming’s impact on children. While previous debates often painted games as harmful, the study revealed significant psychological benefits, particularly for adolescents using consoles like the Nintendo Switch. This nuanced perspective urges policymakers to reconsider blanket assumptions about gaming’s role in young lives.
Although the data was collected during the unique context of the pandemic, the study’s findings have broader implications.
By demonstrating a causal link between gaming and mental well-being, the research paves the way for future studies to explore personalized gaming experiences. Digital media scholars advocate for such tailored approaches, viewing them as a pathway to targeted mental health interventions.
The findings also hold valuable insights for global organizations like the WHO and UNICEF. Policymakers can use this evidence to develop more balanced strategies for managing digital media consumption.
Instead of framing gaming solely as a potential health risk, these strategies could emphasize its therapeutic potential, particularly when carefully moderated and tailored to individual needs.
As gaming continues to evolve, so too must the research methods used to understand its impacts. This study marks a critical step forward, offering a scientifically rigorous perspective on a divisive topic.
By embracing innovative methodologies and diverse viewpoints, researchers and policymakers can better navigate the complex interplay between digital media and human well-being.
Note: Materials provided above by The Brighter Side of News. Content may be edited for style and length.
Like these kind of feel good stories? Get The Brighter Side of News' newsletter.
Rebecca Shavit
Science & Technology Journalist | Innovation Storyteller
Based in Los Angeles, Rebecca Shavit is a dedicated science and technology journalist who writes for The Brighter Side of News, an online publication committed to highlighting positive and transformative stories from around the world. With a passion for uncovering groundbreaking discoveries and innovations, she brings to light the scientific advancements shaping a better future. Her reporting spans a wide range of topics, from cutting-edge medical breakthroughs and artificial intelligence to green technology and space exploration. With a keen ability to translate complex concepts into engaging and accessible stories, she makes science and innovation relatable to a broad audience.