Scientists finally discovered where and when wine grapes first originated
Scientists found fossilized seeds representing nine separate species of grapes, ranging in age from about 20 million to 60 million years old
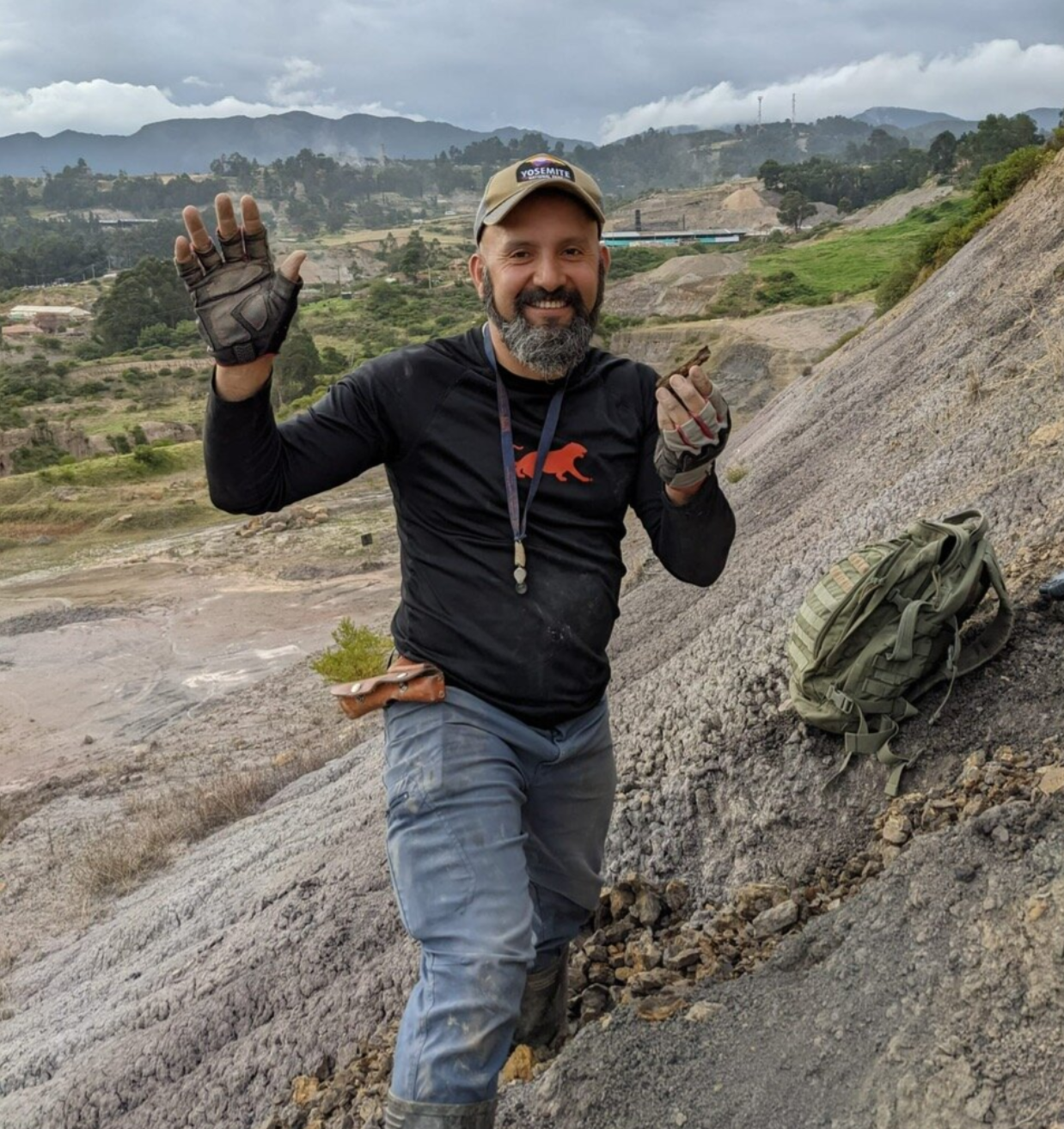

Lead author Fabiany Herrera holding a fossil of the oldest grape ever found in the Western Hemisphere. (CREDIT: Fabiany Herrera)
The ancestor of Vitoid grapes, which led to commercial grape varieties, likely originated in the New World, specifically the tropical belt of the Americas and the Caribbean, around 60 million years ago, according to a study co-authored by a University of Michigan researcher.
Researchers found fossilized seeds representing nine separate species of grapes, ranging in age from about 20 million to 60 million years old, in Panama, Colombia, and Peru. The oldest of these seeds came from plants related to the current subfamily Vitoideae, the same subfamily to which commercial grapes belong, says U-M paleobotanist Mónica Carvalho, co-author of the study published in Nature Plants.
“In excavating the fossil record in the New World tropics, we found seeds related to the grape family dating back 60 million years. This led us to revise the fossil record of grapes in the New World. The oldest seed we found is closely related to the group that gave rise to commercial grapes, the subfamily Vitoideae,” said Carvalho, assistant professor of earth and environmental sciences and assistant curator at the U-M Museum of Paleontology.
“We have this rich but previously poorly known fossil record for grapes in the New World. What we’re seeing is that this family has a complex history of extinction and dispersal. Various groups of this family, such as the genus Leea and species of tribe Cayrateae, only live today in Southeast Asia and the Indo-Pacific, but their fossils indicate they lived in the New World for a long time before becoming regionally extinct.”
Approximately 66 million years ago, at the end of the Cretaceous Period, an asteroid hit Earth. This event, which caused the extinction of dinosaurs, also “pretty much wiped out a lot of the preexisting forests that were living in the tropical latitudes of the New World,” Carvalho says.
New rainforests grew in the destroyed landscape, prompting the diversification of many modern plant and animal groups. Carvalho and lead author Fabiany Herrera, a paleobotanist at the Field Museum of Natural History in Chicago, examined the fossil record from this period to understand the evolution of modern rainforests.
Related Stories
“Within these early neotropical rainforests, we find the earliest record of Vitoideae, indicating that the lineage of grapes dates back to the origin of the first neotropical rainforests,” Carvalho said.
Herrera says the discovery is important “because it shows that after the extinction of the dinosaurs, grapes really started to spread across the world.”
The grape family has an extensive fossil record that predates the Cretaceous extinction event, Carvalho says. The oldest grapes go back to the age of dinosaurs and were found in India. Seeds from these plants may have been borne by animals to the New World.
“The diversification of birds and mammals following the end-Cretaceous extinction could have aided in the dispersal of their seeds,” Herrera said.
Carvalho says their study fills in the history of grapes in the Americas and Caribbean.
“There was a significant gap in the fossil record of grapes after the extinction of dinosaurs. By about 50 million years ago, we see fossil grapes in North America and Europe,” she said. “At that time, when the planet was warmer, grapes had a wider distribution in high northern latitudes, but we didn’t know much about the history of this group in tropical latitudes. That’s where our work comes in.”
This study reveals the complex history of grape dispersal and extinction in the New World, highlighting the ancient origins and widespread distribution of grape ancestors long before they became the commercial varieties we know today. This research not only revises the fossil record of grapes but also sheds light on the broader patterns of plant evolution and migration in response to major climatic and geological events.
Note: Materials provided above by the The Brighter Side of News. Content may be edited for style and length.
Like these kind of feel good stories? Get the Brighter Side of News' newsletter.
Joseph Shavit
Head Science News Writer | Communicating Innovation & Discovery
Based in Los Angeles, Joseph Shavit is an accomplished science journalist, head science news writer and co-founder at The Brighter Side of News, where he translates cutting-edge discoveries into compelling stories for a broad audience. With a strong background spanning science, business, product management, media leadership, and entrepreneurship, Joseph brings a unique perspective to science communication. His expertise allows him to uncover the intersection of technological advancements and market potential, shedding light on how groundbreaking research evolves into transformative products and industries.