New wearable device enhances deep sleep
Many people, especially the elderly, suffer from abnormal sleep. In particular, the deep sleep phases become shorter and shallower with age.
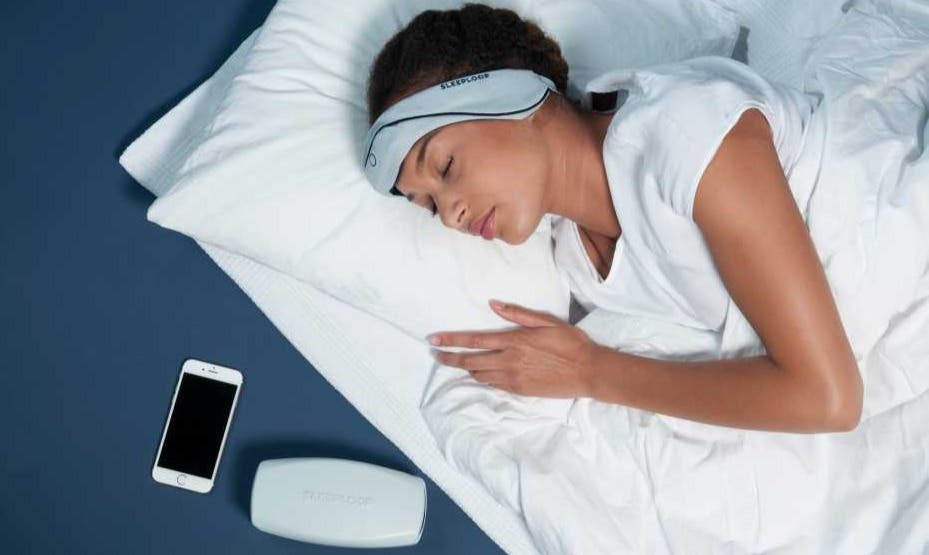

[Apr 10, 2022: Peter Rueegg, ETH Zurich]
The SleepLoop system developed by ETH Zurich researchers emits a sound at the right time to amplify the slow brain waves. (CREDIT: Sleeploop)
Researchers have developed a wearable device that plays specific sounds to enhance deep sleep. The first clinical study has now shown that the device is effective, but not at the same level of effectiveness for everyone.
Many people, especially the elderly, suffer from abnormal sleep. In particular, the deep sleep phases become shorter and shallower with age. Deep sleep is important for the regeneration of the brain and memory, and also has a positive influence on the cardiovascular system.
Researchers have shown that the brain waves characterizing deep sleep, so-called slow waves, can be improved by playing precisely timed sounds through earphones while sleeping. While this works well in the sleep laboratory under controlled conditions, there has thus far been no at home solution that can be used longer than just one night.
SleepLoop to the rescue
As part of the SleepLoop project, researchers at ETH Zurich have developed a mobile system that can be used at home and aims to promote deep sleep through auditory brain stimulation.
The SleepLoop system consists of a headband that is put on at bedtime and worn throughout the night. This headband contains electrodes and a microchip that constantly measure the brain activity of the person sleeping. Data from this is analysed autonomously in real-time on the microchip using custom software. As soon as the sleeping person shows slow waves in the brain activity characterising deep sleep, the system triggers a short auditory signal (clicking). This helps to synchronise the neuronal cells and enhance the slow waves. What makes the solution unique is that the person sleeping is not conciously aware of this sound during deep sleep.
Related Stories:
The first clinical study
Researchers from ETH Zurich and University Hospital Zurich, led by Caroline Lustenberger, group leader at the Neural Control of Movement Lab, have conducted a clinical study with this device for the first time. The results have just been published in the journal Communications Medicine.
The study involved equipping participants, between 60 – 80 years old, with the SleepLoop system, which they were required to operate themselves in their own home. The system is designed to function independently even by users with little technical experience. “This worked very well. We had surprisingly little data loss and the participants rated the device as user-friendly,” says Lustenberger.
They wore the device every night for a total of four weeks, with the auditory stimulation given on a nightly basis for two weeks and no stimulation for the next two weeks. Neither the subjects nor the researchers knew in which two weeks the auditory signals were played and in which two they were not.
Auditory stimulation is indeed feasible
The results of 16 participants of the study show that it was indeed possible to enhance the slow waves through auditory signals during deep sleep in most participants. However, the individual differences were extensive with some of the subjects responding very well to the stimuli, while others responded minimally or not at all.
According to Lustenberger, the question of whether a person reacted to a stimulus did not depend on their well-being during the day. “Some people generally responded well to the stimuli and clearly showed enhanced slow waves, while others showed no response, regardless of their daily well-being.”
The researchers have used these individual differences to better predict how a given individual will respond to the auditory stimulus. This in turn helps them to optimise and improve the performance of SleepLoop.
On track for market launch
A spin-off company Tosoo AG, is currently working on developing the device further and preparing it for the clinical market. It is already clear that it will not be freely available, but only via a doctor’s prescription.
“This is a medical device, not just a wellness consumer product you can order online when you have trouble sleeping,” emphasises Walter Karlen, who developed the technology at ETH Zurich.
Note: Materials provided above by ETH Zurich. Content may be edited for style and length.
Like these kind of feel good stories? Get the Brighter Side of News' newsletter.
Tags: #New_Innovations, #Medical_News, #Sleep, #Science, #Wearable_Device, #Research, #Neuroscience, #Brain, #Technology, #The_Brighter_Side_of_News
Joseph Shavit
Head Science News Writer | Communicating Innovation & Discovery
Based in Los Angeles, Joseph Shavit is an accomplished science journalist, head science news writer and co-founder at The Brighter Side of News, where he translates cutting-edge discoveries into compelling stories for a broad audience. With a strong background spanning science, business, product management, media leadership, and entrepreneurship, Joseph brings a unique perspective to science communication. His expertise allows him to uncover the intersection of technological advancements and market potential, shedding light on how groundbreaking research evolves into transformative products and industries.