Nanotechnology turns bricks into batteries
Red bricks — some of the world’s cheapest and most familiar building materials — can be converted into energy storage units.
[Apr. 26, 2022: Talia Ogliore]
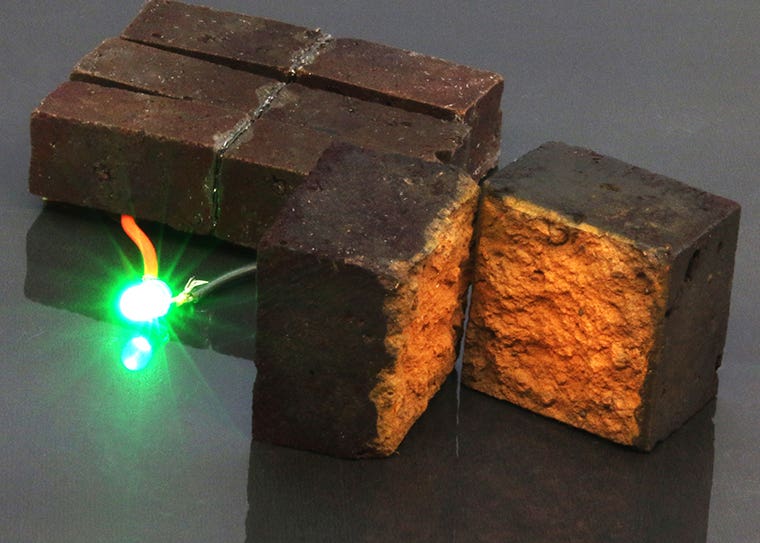
Chemists in Arts & Sciences have developed a method to make or modify “smart bricks” that can store energy until required for powering devices. (CREDIT: D’Arcy laboratory)
Imagine plugging in to your brick house.
Red bricks — some of the world’s cheapest and most familiar building materials — can be converted into energy storage units that can be charged to hold electricity, like a battery, according to new research from Washington University in St. Louis.
Brick has been used in walls and buildings for thousands of years, but rarely has been found fit for any other use. Now, chemists in Arts & Sciences have developed a method to make or modify “smart bricks” that can store energy until required for powering devices. A proof-of-concept published in Nature Communications (and pictured above) shows a brick directly powering a green LED light.
“Our method works with regular brick or recycled bricks, and we can make our own bricks as well,” said Julio D’Arcy, assistant professor of chemistry. “As a matter of fact, the work that we have published in Nature Communications stems from bricks that we bought at Home Depot right here in Brentwood (Missouri); each brick was 65 cents.”
Walls and buildings made of bricks already occupy large amounts of space, which could be better utilized if given an additional purpose for electrical storage. While some architects and designers have recognized the humble brick’s ability to absorb and store the sun’s heat, this is the first time anyone has tried using bricks as anything more than thermal mass for heating and cooling.
Related Stories
D’Arcy and colleagues, including Washington University graduate student Hongmin Wang, first author of the new study, showed how to convert red bricks into a type of energy storage device called a supercapacitor.
“In this work, we have developed a coating of the conducting polymer PEDOT, which is comprised of nanofibers that penetrate the inner porous network of a brick; a polymer coating remains trapped in a brick and serves as an ion sponge that stores and conducts electricity,” D’Arcy said.
The red pigment in bricks — iron oxide, or rust — is essential for triggering the polymerisation reaction. The authors’ calculations suggest that walls made of these energy-storing bricks could store a substantial amount of energy.
“PEDOT-coated bricks are ideal building blocks that can provide power to emergency lighting,” D’Arcy said. “We envision that this could be a reality when you connect our bricks with solar cells — this could take 50 bricks in close proximity to the load. These 50 bricks would enable powering emergency lighting for five hours.
“Advantageously, a brick wall serving as a supercapacitor can be recharged hundreds of thousands of times within an hour. If you connect a couple of bricks, microelectronics sensors would be easily powered.”
Note: Materials provided above by Washington University in St. Louis. Content may be edited for style and length.
Like these kind of feel good stories? Get the Brighter Side of News' newsletter.
Tags: #New_Innovations, #Green_Good_News, #Batteries, #Clean_Energy, #Technology, #Research, #Bricks, #Construction, #The_Brighter_Side_of_News
Joseph Shavit
Head Science News Writer | Communicating Innovation & Discovery
Based in Los Angeles, Joseph Shavit is an accomplished science journalist, head science news writer and co-founder at The Brighter Side of News, where he translates cutting-edge discoveries into compelling stories for a broad audience. With a strong background spanning science, business, product management, media leadership, and entrepreneurship, Joseph brings a unique perspective to science communication. His expertise allows him to uncover the intersection of technological advancements and market potential, shedding light on how groundbreaking research evolves into transformative products and industries.