Groundbreaking treatment for heart disease uses lasers to vaporize blockages
Researchers developed a method that combines a low-power laser with ultrasound to remove arterial plaque safely and efficiently.
[Mar. 3, 2023: Larry Frum, American Institute of Physics]
Researchers developed a method that combines a low-power laser with ultrasound to remove arterial plaque safely. (CREDIT: iStock Photos)
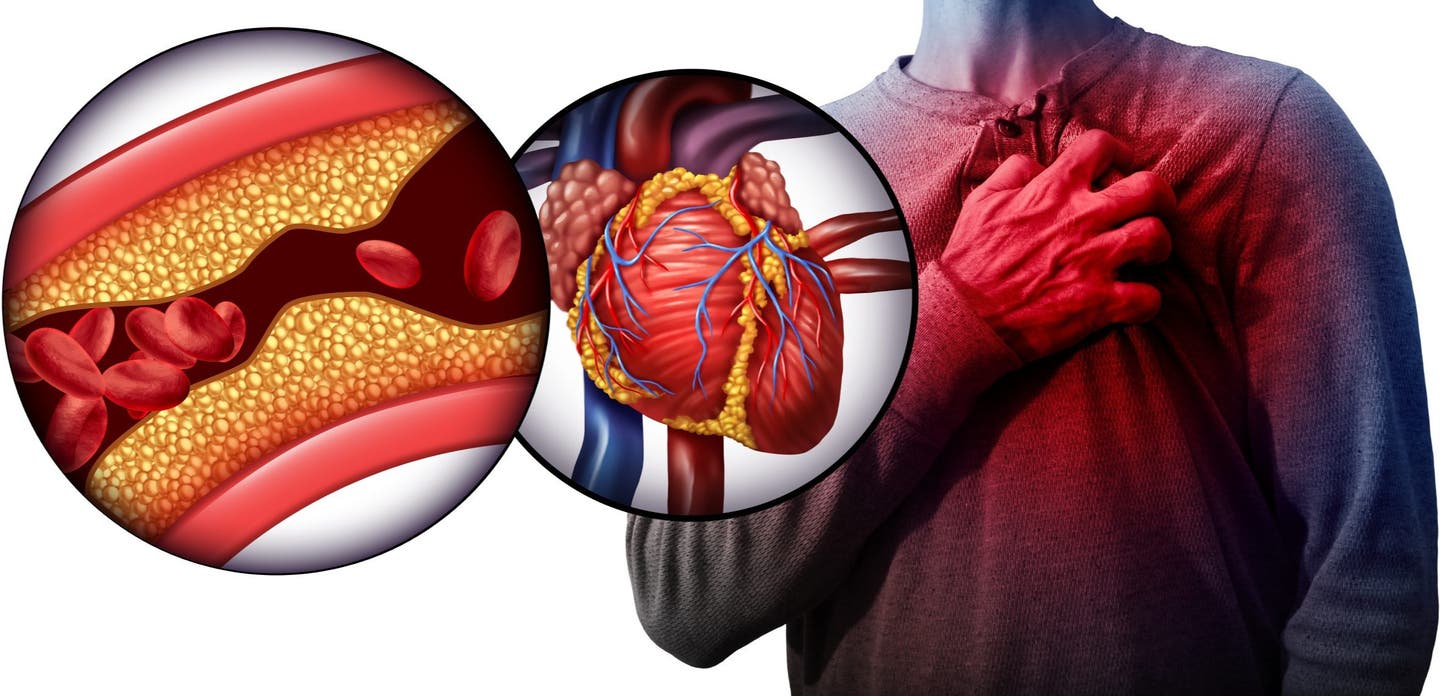
Atherosclerosis, a buildup of plaque, can lead to heart disease, artery disease, and chronic kidney disease and is traditionally treated by inserting and inflating a balloon to expand the artery. Other treatments based on lasers can remove blockages rather than simply compressing them but are used infrequently, because they have a high risk of complication and low efficacy.
Rohit Singh, of the University of Kansas, and other researchers developed a method that combines a low-power laser with ultrasound to remove arterial plaque safely and efficiently.
High-power laser treatments direct thermal energy to vaporize water in the artery and create a vapor bubble, which expands and collapses to break the plaque. Similarly, the technology, pioneered by Xinmai Yang, doctoral advisor for the team, uses a low-power nanosecond pulsed laser to produce microbubbles. The addition of irradiation from ultrasound causes the microbubbles to expand, collapse, and disrupt the plaque.
"In conventional laser angioplasty, a high laser power is required for the entire cavitation process, whereas in our technology, a lower laser power is only required for initiating the cavitation process," said Singh. "Overall, the combination of ultrasound and laser reduces the need for laser power and improves the efficiency of atherosclerotic plaque removal."
Related Stories
Because it destroys rather than compresses the plaque, the combination technique will have a lower restenosis rate, or re-narrowing of the artery, compared to balloon angioplasty or stenting. The control provided by the ultrasound and the low-power laser will lower the risk of dissection and perforation in arteries.
Atherosclerosis, a buildup of plaque, can lead to heart disease, artery disease, and chronic kidney disease and is traditionally treated by inserting and inflating a balloon to expand the artery. (CREDIT: Rohit Singh, University of Kansas)
The team performed ex vivo experiments on carotid artery plaque samples and pork belly samples, and they are currently planning to perform in vivo experiments. Both the laser and ultrasound techniques are commonly used by clinicians and should be easy to teach and implement following the in vivo studies.
Combining low-power lasers and ultrasound techniques is not limited to atherosclerosis treatments. Singh and collaborators are also using the methodology for photo-mediated ultrasound therapy and ultrasound-assisted endovascular laser thrombolysis. The former can be used to remove abnormal microvessels in the eye to prevent blindness, while the latter can dissolve blood clots in veins.
Symptoms of heart disease
Heart disease symptoms depend on the type of heart disease.
Coronary artery disease is a common heart condition that affects the major blood vessels that supply the heart muscle. Cholesterol deposits (plaques) in the heart arteries are usually the cause of coronary artery disease. The buildup of these plaques is called atherosclerosis (ath-ur-o-skluh-ROE-sis). Atherosclerosis reduces blood flow to the heart and other parts of the body. It can lead to a heart attack, chest pain (angina) or stroke.
Coronary artery disease symptoms may be different for men and women. For instance, men are more likely to have chest pain. Women are more likely to have other symptoms along with chest discomfort, such as shortness of breath, nausea and extreme fatigue.
Symptoms of coronary artery disease can include:
Chest pain, chest tightness, chest pressure and chest discomfort (angina)
Shortness of breath
Pain in the neck, jaw, throat, upper belly area or back
Pain, numbness, weakness or coldness in the legs or arms if the blood vessels in those body areas are narrowed
Heart disease symptoms caused by irregular heartbeats (heart arrhythmias)
The heart may beat too quickly, too slowly or irregularly. Heart arrhythmia symptoms can include:
Chest pain or discomfort
Dizziness
Fainting (syncope) or near fainting
Fluttering in the chest
Lightheadedness
Racing heartbeat (tachycardia)
Shortness of breath
Slow heartbeat (bradycardia)
Heart disease symptoms caused by congenital heart defects
Serious congenital heart defects usually are noticed soon after birth. Congenital heart defect symptoms in children could include:
Pale gray or blue skin or lips (cyanosis)
Swelling in the legs, belly area or areas around the eyes
In an infant, shortness of breath during feedings, leading to poor weight gain
Less-serious congenital heart defects are often not diagnosed until later in childhood or during adulthood. Symptoms of congenital heart defects that usually aren't immediately life-threatening include:
Easily getting short of breath during exercise or activity
Easily tiring during exercise or activity
Swelling of the hands, ankles or feet
Heart disease symptoms caused by diseased heart muscle (cardiomyopathy)
Early stages of cardiomyopathy may not cause noticeable symptoms. As the condition worsens, symptoms may include:
Dizziness, lightheadedness and fainting
Fatigue
Feeling short of breath during activity or at rest
Feeling short of breath at night when trying to sleep or waking up short of breath
Irregular heartbeats that feel rapid, pounding or fluttering
Swollen legs, ankles or feet
Heart disease symptoms caused by heart valve problems (valvular heart disease)
The heart has four valves — the aortic, mitral, pulmonary and tricuspid valves. They open and close to move blood through the heart. Many things can damage the heart valves. A heart valve may become narrowed (stenosis), leaky (regurgitation or insufficiency) or close improperly (prolapse).
Valvular heart disease is also called heart valve disease. Depending on which valve isn't working properly, heart valve disease symptoms generally include:
Chest pain
Fainting (syncope)
Fatigue
Irregular heartbeat
Shortness of breath
Swollen feet or ankles
Endocarditis is an infection that affects the heart valves and inner lining of the heart chambers and heart valves (endocardium). Endocarditis symptoms can include:
Dry or persistent cough
Fever
Heartbeat changes
Shortness of breath
Skin rashes or unusual spots
Swelling of the legs or belly area
Weakness or fatigue
You might not be diagnosed with coronary artery disease until you have a heart attack, angina, stroke or heart failure. It's important to watch for heart symptoms and discuss concerns with your health care provider. Heart (cardiovascular) disease can sometimes be found early with regular health checkups.
For more science and technology news stories check out our New Innovations section at The Brighter Side of News.
Note: Materials provided above by American Institute of Physics. Content may be edited for style and length.
Like these kind of feel good stories? Get the Brighter Side of News' newsletter.
Joseph Shavit
Head Science News Writer | Communicating Innovation & Discovery
Based in Los Angeles, Joseph Shavit is an accomplished science journalist, head science news writer and co-founder at The Brighter Side of News, where he translates cutting-edge discoveries into compelling stories for a broad audience. With a strong background spanning science, business, product management, media leadership, and entrepreneurship, Joseph brings a unique perspective to science communication. His expertise allows him to uncover the intersection of technological advancements and market potential, shedding light on how groundbreaking research evolves into transformative products and industries.



