Can ‘random noise’ unlock our learning potential?
Edith Cowan University has investigated the effects of transcranial random noise stimulation (tRNS) in a variety of settings.

[Sept 25, 2022: Sam Jeremic, Edith Cowan University]
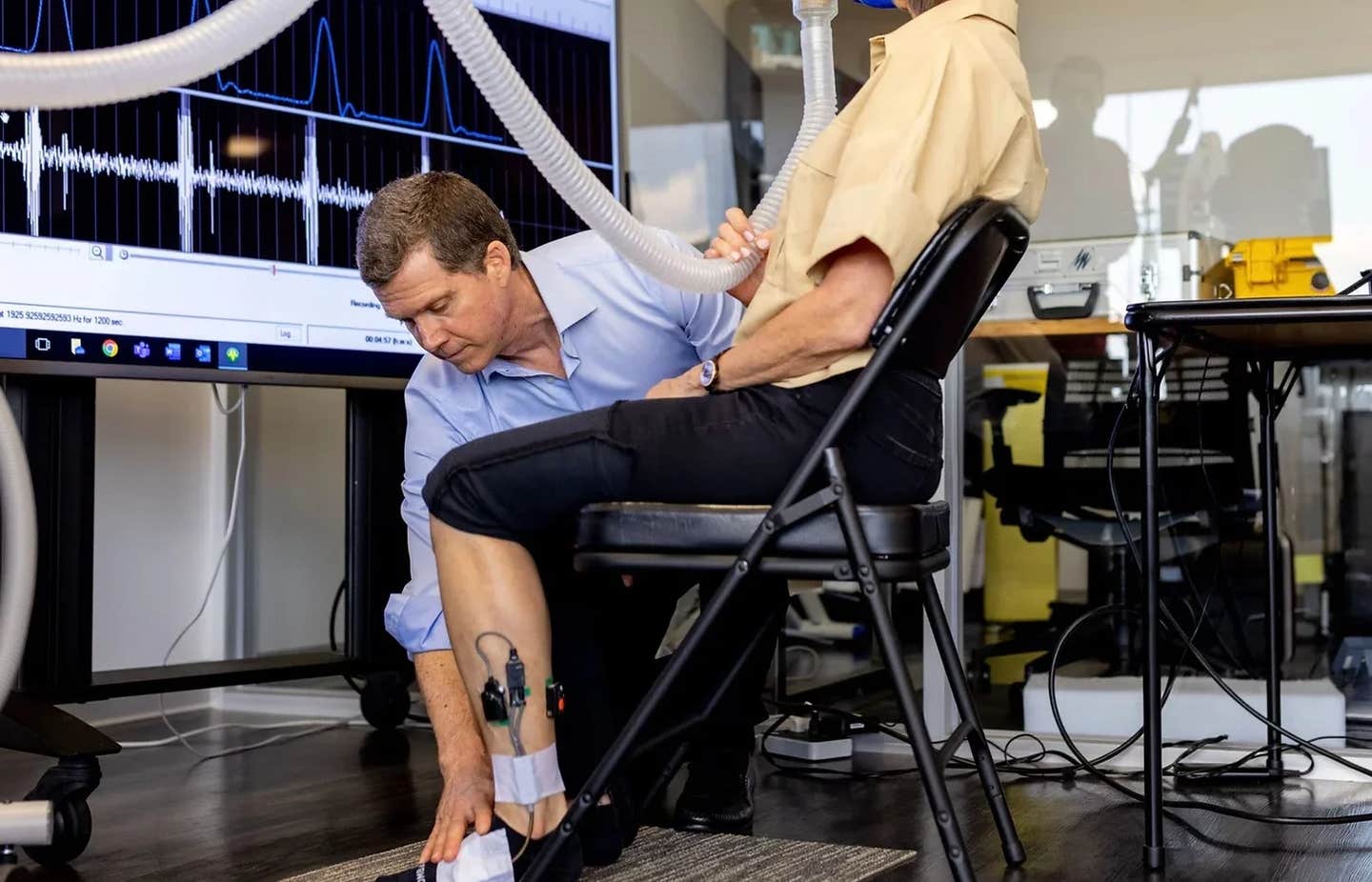
Study showed tRNS has promise as a tool to assist people with compromised learning capabilities. (CREDIT: Creative Commons)
Though many of us may seek a quiet place in which to study, ‘noise’ may play a key role in helping some people improve their learning potential.
Edith Cowan University (ECU) has investigated the effects of transcranial random noise stimulation (tRNS) in a variety of settings and found the technology could have many applications.
Despite its name, tRNS doesn’t utilize noise in the everyday, auditory sense of the word.
Rather, it sees electrodes attached to the head so a weak current can pass through specific parts of the brain.
Study lead Dr Onno van der Groen said the study showed tRNS has promise as a tool to assist people with compromised learning capabilities.
“The effect on learning is promising: it can speed up learning and help people with neurological conditions,” Dr van der Groen said.
Related Stories:
“So, people with learning difficulties you can use it to enhance learning rate, for example.
“It’s also been trialled on people with visual deficits, such as after stroke and traumatic brain injury.
“When you add this type of stimulation during learning, you get better performance, faster learning and better attention afterwards as well.”
Forming new pathways
Dr van der Groen said tRNS works by allowing the brain to form new connections and pathways, a process known as neuroplasticity.
Transcranial random noise stimulation (tRNS). A) An example of a tRNS electrode montage and its modeled electrical field strength (normE) targeting the visual cortex. B) A random level of current is generated for every sample (sampling rate 1280 Hz). The random numbers are from a normal distribution and the average current applied is 0. This image shows a signal which is 2 mA peak-to-peak, i.e., with 99% of all generated amplitude values between −1 and 1 mA. The histogram shows the normal distribution with a zero-mean. Credit: Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews (2022). DOI: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2022.104702
“If you learn something, there has to be neuroplastic changes in your brain, which allows you to learn this information,” he said.
“And this is a tool to enhance this neuroplasticity.”
Dr van der Groen said tRNS had two effects on the brain: the ‘acute’ effect, which allows a person to perform better while undergoing tRNS, and the modulating effect which saw lasting results.
Overview of the stochastic resonance concept. A) An optimal level of noise can allow a weak subthreshold signal to cross a threshold for detection. When too much noise is added the signal will be masked by the excessive noise (from Miniussi et al. (2013)). B) This image shows how the output signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) changes with increasing noise levels. The dose-response relationship between noise level and SNR is characterized by an inverted-U shape function.
“If you do 10 sessions of a visual perception task with the tRNS and then come back and do it again without it, you’ll find you perform better than the control group who hasn’t used it,” he said.
“Limitless” potential?
The idea of expanding one’s learning potential via tech such as tRNS raises many questions.
While it’s most pertinent to those with deficiencies and difficulties in learning, it also begs the question as to whether a neurotypical person can take their intelligence to new levels, similar to the concept in the movie ‘Limitless’.
Dr van der Groen says the potential is there, but there are also signs it won’t create a ‘new level’ of intelligence.
The question is, if you’re neurotypical, are you already performing at your peak,” he said.
“There’s a case study where they tried to enhance the mathematical skills of a super mathematician; with him, it didn’t have much of an impact on his performance, presumably because he is already a top performer in that area.
“But it could be used if you’re learning something new.”
Where it’s headed
Though the technology is still in its infancy and people are only able to access tRNS by entering controlled trials, Dr van der Groen said its practicality and apparent safety meant there was a lot of potential for a range of applications.
“The concept is relatively simple,” he said.
“It’s like a battery: the current runs from plus to minus, but it goes through your head as well.
“We’re working on a study where we send the equipment to people, and they apply everything themselves remotely.
“So in that regards, it’s quite easy to use.”
Scientists worldwide are also investigating tRNS’ effects on perception, working memory, sensory processing and other aspects of behaviour, with the technology showing promise as a treatment for a range of clinical conditions.
“We’re still trying to find out how best we can use it,” Dr van der Groen said.
‘Using noise for the better :The effects of transcranial random noise stimulation on the brain and behaviour’ was published in Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews.
Note: Materials provided above by Edith Cowan University. Content may be edited for style and length.
Like these kind of feel good stories? Get the Brighter Side of News' newsletter.
Joshua Shavit
Science & Technology Writer | AI and Robotics Reporter
Joshua Shavit is a Los Angeles-based science and technology writer with a passion for exploring the breakthroughs shaping the future. As a contributor to The Brighter Side of News, he focuses on positive and transformative advancements in AI, technology, physics, engineering, robotics and space science. Joshua is currently working towards a Bachelor of Science in Business Administration at the University of California, Berkeley. He combines his academic background with a talent for storytelling, making complex scientific discoveries engaging and accessible. His work highlights the innovators behind the ideas, bringing readers closer to the people driving progress.