Breakthrough study shows the importance of well-being in reducing heart disease deaths
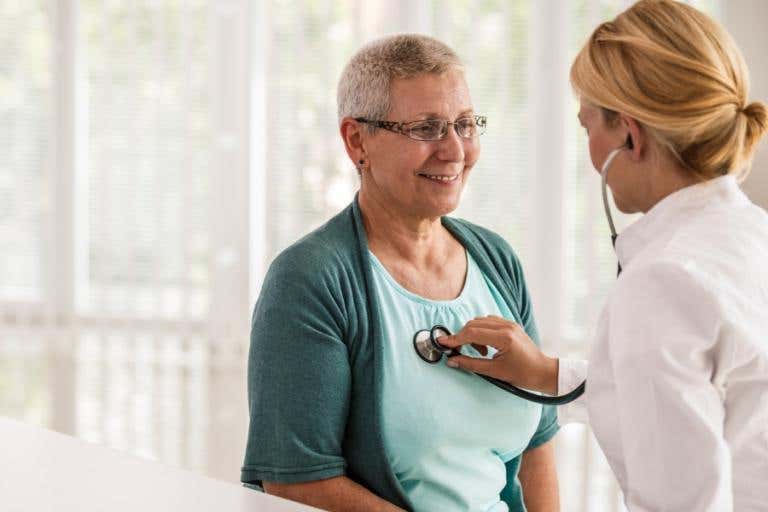
The findings suggest that focusing on community well-being can have a significant impact on reducing cardiovascular deaths.

[July 6, 2023: Staff Writer, The Brighter Side of News]
The findings suggest that focusing on community well-being can have a significant impact on reducing cardiovascular deaths. (CREDIT: Creative Commons)
Heart disease remains a leading cause of death in the United States, but the factors contributing to its prevalence and mortality rates are not solely limited to traditional risk factors such as high blood pressure and diabetes.
A recent study conducted by researchers at Yale University explored the association between population well-being and cardiovascular disease (CVD) mortality, shedding light on the potential of well-being as a crucial factor in improving heart health outcomes. The findings suggest that focusing on community well-being can have a significant impact on reducing cardiovascular deaths.
The study, published in JAMA Network Open, analyzed data from the Gallup National Health and Well-Being Index (WBI) survey and county-level rates of CVD mortality from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The survey collected responses from over 514,000 individuals across 3,228 counties in the United States between 2015 and 2017. Researchers investigated the relationship between population well-being and rates of CVD mortality while considering various structural and health factors.
The study revealed a clear association between population well-being and CVD mortality rates. Counties with higher well-being scores exhibited lower mortality rates from cardiovascular conditions such as heart failure, stroke, coronary heart disease, and acute myocardial infarction. The analysis accounted for various factors, including income inequality, urbanicity, hypertension, diabetes, obesity, smoking rates, and physical inactivity.
Related Stories
Moreover, the study found that even after controlling for structural and health factors, the association between well-being and CVD mortality remained significant. For every one-point increase in well-being on the WBI scale, the CVD death rate decreased by 7.3 deaths per 100,000 persons. This suggests that enhancing well-being at the community level can independently contribute to improving cardiovascular health.
Well-being, as defined by the Gallup WBI survey, encompasses multiple dimensions such as a sense of purpose, social relationships, financial security, and connection to the community.
Living in a community with high well-being can potentially mitigate the negative effects of stress and improve overall health throughout an individual's lifespan. Factors contributing to well-being include access to healthcare and social services, safe and clean environments, transportation options, green spaces, and healthy food options.
Scatter Plot of County Cardiovascular Disease Mortality Rate vs Modified Well-Being Index. (CREDIT: JAMA)
Importantly, the study highlights that well-being is not solely determined by economic status but can be influenced by other modifiable community factors. This suggests that community engagement, collective action, and public policy can play a crucial role in improving well-being and, consequently, cardiovascular health outcomes.
The findings of this study hold significant implications for public health interventions aimed at reducing cardiovascular disease mortality rates. Traditional approaches that focus solely on individual risk factors may benefit from a shift towards a more holistic perspective that considers community well-being. By addressing social determinants of health and fostering supportive environments, communities can potentially create conditions that promote better heart health and reduce health disparities.
Summary of Cardiovascular Disease Mortality Rates (Per 100 000 Persons) for All Counties and by Q of Overall Modified WBI. (CREDIT: JAMA)
The study also suggests the importance of developing interventions and policies targeting the specific elements of well-being that have the greatest impact on cardiovascular health outcomes. In this study, community and financial well-being were found to be particularly influential in reducing CVD mortality rates. Tailored initiatives addressing these aspects may yield positive results in terms of improving heart health at the population level.
While this study provides valuable insights, it is important to note that it is cross-sectional in nature and cannot establish causality. Further research is needed to examine the long-term effects of interventions targeting community well-being and their impact on cardiovascular health outcomes.
Association of Modified WBI, Index Elements, and Life Evaluation Scores With Cardiovascular Outcomes. (CREDIT: JAMA)
Additionally, expanding this research to include diverse populations and geographical areas could help identify specific community factors that contribute to well-being and cardiovascular health.
In conclusion, this study emphasizes the importance of population well-being in reducing cardiovascular disease mortality rates. By focusing on community-level factors and implementing interventions that promote well-being, we have the potential to make significant strides in improving heart health and fostering healthier communities overall.
For more science and technology stories check out our New Discoveries section at The Brighter Side of News.
Note: Materials provided above by The Brighter Side of News. Content may be edited for style and length.
Like these kind of feel good stories? Get the Brighter Side of News' newsletter.