Anti-cancer drug shows incredible promise in human clinical trials
PAC-1, a drug originally developed by scientists at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, triggers programmed cell death in cancer cells.
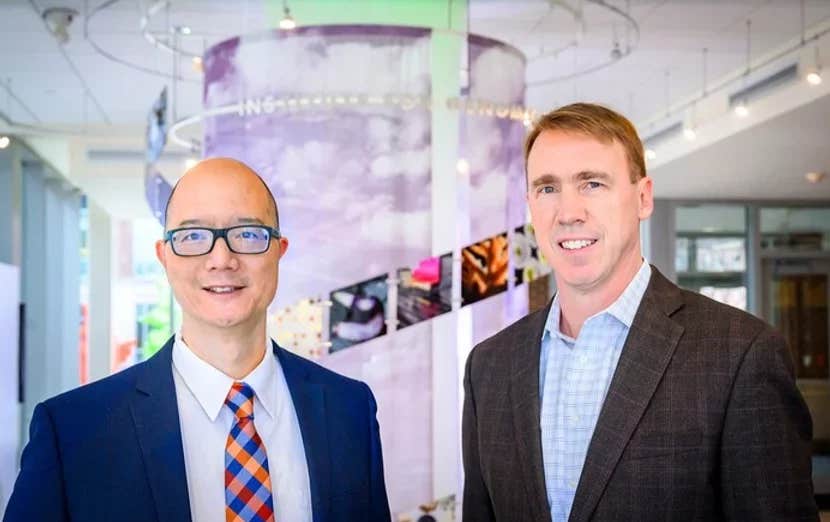

U. of I. researchers. Illinois professor of veterinary clinical medicine Dr. Timothy Fan, left, and chemistry professor Paul Hergenrother. The U. of I. team found that the compound PAC-1 has therapeutic potential in pet dogs with spontaneously occurring cancers. The animal studies set the stage for the human clinical trials. (CREDIT: Fred Zwicky)
For decades, the medical world has avidly searched for groundbreaking treatments against one of humanity’s most resilient foes: cancer. Today, that search might be inching closer to a significant discovery, as a recent phase I clinical trial of PAC-1 has exhibited potential to combat various cancer types, revealing only minor side effects.
PAC-1, a drug originally developed by scientists at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, triggers programmed cell death in cancer cells.
Most notably, it managed to halt tumor growth in five participants suffering from neuroendocrine cancers. Impressively, two of these patients witnessed a reduction in tumor size. The drug also demonstrated therapeutic activity against sarcomas, as noted in the British Journal of Cancer.
Phase I clinical trials, as Dr. Arkadiusz Dudek, the study's clinical director, highlights, primarily evaluate new drug compounds for concerning side effects or toxicities in humans. Dudek, affiliated with HealthPartners Cancer Center at Regions Hospital, St. Paul, Minnesota, and Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota, remarked on the trial's significance, given its testing on a limited patient pool, all of whom had advanced stages of various cancers.
Dudek stated, “We had patients with colon cancer, breast cancer, pancreatic cancer, adenocarcinoma, melanoma and others.”
This trial, alongside another examining PAC-1’s effectiveness against brain cancer, is a collaborative effort involving Regions Hospital, the University of Illinois Chicago, and Johns Hopkins University.
Related Stories
The phase I process, as explained by Dr. Oana Danciu of the University of Illinois Cancer Center in Chicago, starts with administering extremely low drug doses to monitor side effects. Over several months, and provided no alarming toxicities arise, doses gradually increase until a potentially therapeutic amount is reached.
PAC-1’s Journey: From Labs to Clinical Trials
The story of PAC-1 began in the early 2000s when University of Illinois researchers identified its anti-cancer potential. Their focus was on the procaspase-3 protein pathway, a pathway suppressed in cancer cells. Chemistry professor Paul Hergenrother and his team discerned that procaspase-3 is prevalent in many cancer cells compared to healthy cells, designating it as a prime target for anti-cancer strategies.
Furthermore, animal trials involving pet dogs with spontaneous lymphomas and other cancers indicated PAC-1’s potential benefits. Such preliminary successes eventually paved the way for human trials, which received significant support from an anonymous angel investor and a biotechnology company, Vanquish Oncology, established by Hergenrother.
What Lies Ahead: The Future of PAC-1 and its Potential in Treating Cancer
Clinicians are actively pursuing additional funds for phase II clinical trials, focusing on a larger, healthier patient pool with closely matching cancer profiles. Their strategic approach is clear. Dr. Dudek shared, “Our strategy is to figure out which tumor type will be the most sensitive and pursue that.” He further expressed enthusiasm over PAC-1's promising results with neuroendocrine tumors, a type lacking extensive drug treatment options.
More insights are also on the horizon from a phase I clinical trial involving PAC-1's potential to treat glioblastoma multiforme, an aggressive brain cancer variant. Crucially, prior research highlighted PAC-1’s ability to cross the blood-brain barrier, an essential trait for any brain cancer remedy.
PAC-1’s Broad Potential in the War Against Cancer
Should further trials prove PAC-1’s efficacy against specific cancer types, resulting in its eventual approval, it would streamline and reduce costs to test against other cancer forms. Such an approved drug could also be available for "off-label use" by medical professionals who believe their patients could benefit from its inclusion in their cancer-treatment protocols.
Nevertheless, the journey from clinical trials to an approved cancer drug is long and intricate. Yet, with the promise that PAC-1 has demonstrated thus far, there remains a beacon of hope in the fight against cancer.


The pursuit of effective cancer treatment is a relentless, global endeavor. PAC-1's recent phase I clinical trial success stories serve as a testament to the potential breakthroughs lying on the horizon. As the world waits with bated breath, this drug may yet become a cornerstone in transforming the narrative of cancer treatment.
Note: Materials provided above by The Brighter Side of News. Content may be edited for style and length.
Like these kind of feel good stories? Get The Brighter Side of News' newsletter.
Joseph Shavit
Head Science News Writer | Communicating Innovation & Discovery
Based in Los Angeles, Joseph Shavit is an accomplished science journalist, head science news writer and co-founder at The Brighter Side of News, where he translates cutting-edge discoveries into compelling stories for a broad audience. With a strong background spanning science, business, product management, media leadership, and entrepreneurship, Joseph brings a unique perspective to science communication. His expertise allows him to uncover the intersection of technological advancements and market potential, shedding light on how groundbreaking research evolves into transformative products and industries.